Punta della Dogana was built in the 17th century and is one of the symbolic buildings in the lagoon city. With its unmistakable triangular shape, it divides the Grand Canal from the Giudecca Canal.
THE PROBLEM
In May 2003, during some restoration work on the bank along the Grand Canal, there was a sudden subsidence of the bank wall and the monumental building of the Dogana behind it. This kinetic motion reopened long-standing cracks and created new ones in the wall lining, load-bearing walls, and stairwell.
Customer needs
The customer needed not only a prompt, long-lasting intervention, but the delicate nature of the context required the choice of a team of professionals capable of working for the utmost protection of historical buildings in a restricted site and under conditions with many operational limits.
Why the Uretek solution was chosen:
- Speed
Careful planning and programming of the times allowed the work to be completed in a relatively short time; - Competitive prices;
- Non-invasive
The intervention proposed by Uretek did not require excavations or masonry work, and it did not dirty the area or produce waste; - Continuous monitoring of the work
Both during and after the intervention, the activities were subject to real-time control by highly qualified personnel using advanced laser technology; - Application of the exclusive Uretek Deep Injections® technology
With the Uretek Geoplus® expanding resin with high swelling pressure, the soil is compacted and the structures stabilized; - Respect for the environment
Above-ground mixing of the Uretek® resin creates a final inert product that does not release solvents into the soil or possible water tables in the area.
THE SOLUTION
We applied the Uretek Deep Injections® technology, injecting Uretek Geoplus® expanding resin into the foundation soil and the ground behind the canal wall, without interfering with the existing wall structures. The intervention took place in two phases:
- PHASE 1 – Surface compaction:
injections were made in the intrados of the foundations to improve the geomechanical characteristics of the terrain and fill the larger voids present in the foundation-soil interface. - PHASE 2 - Deep consolidation:
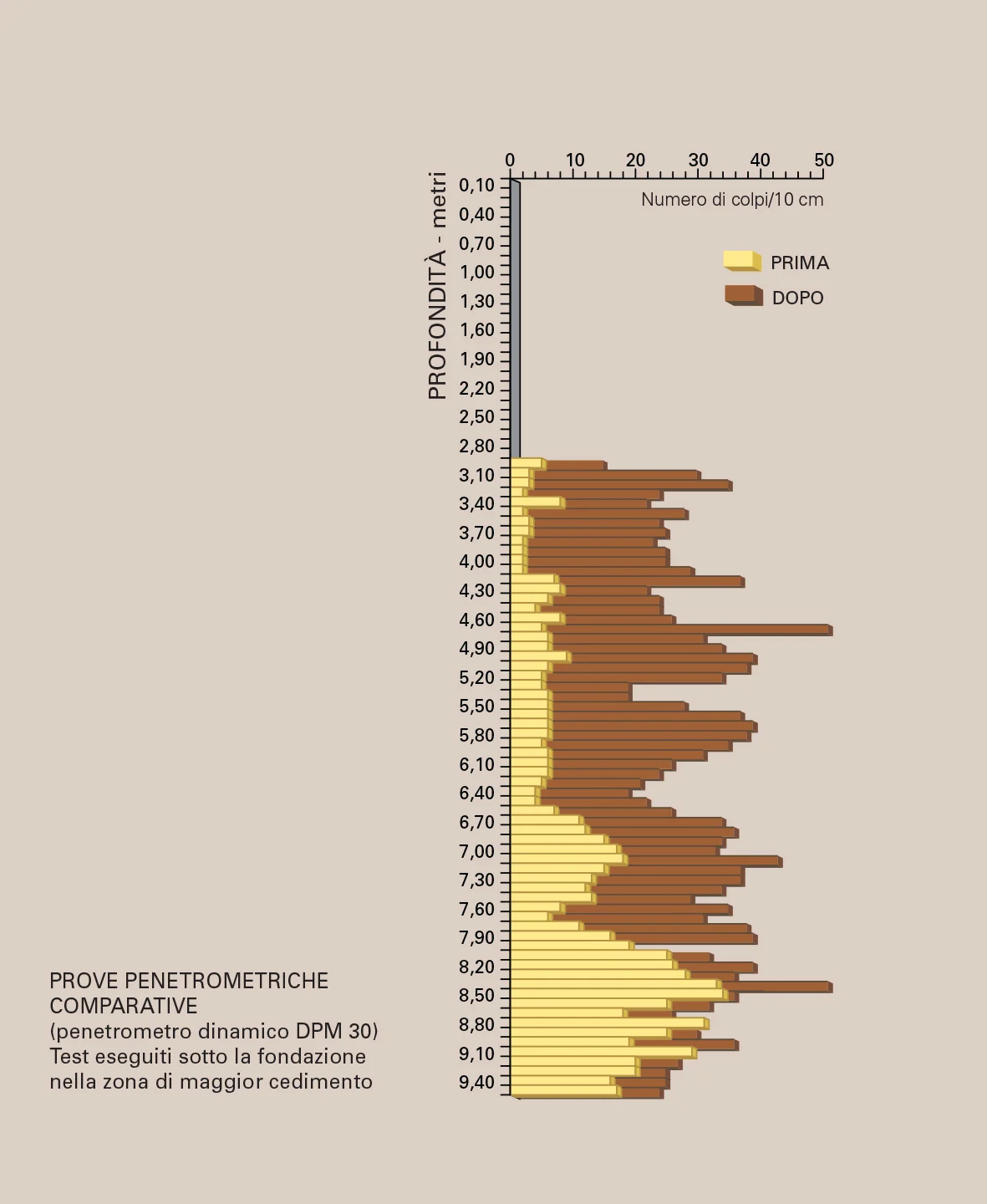
injections into the volume of soil affected by the loads above until the roof of the sandy formation is reached. We verified the success of the intervention via laser monitoring during the injections, penetration tests made before and after the intervention, and material sampling for laboratory tests.
THE INTERVENTION IN DETAIL
The investigations
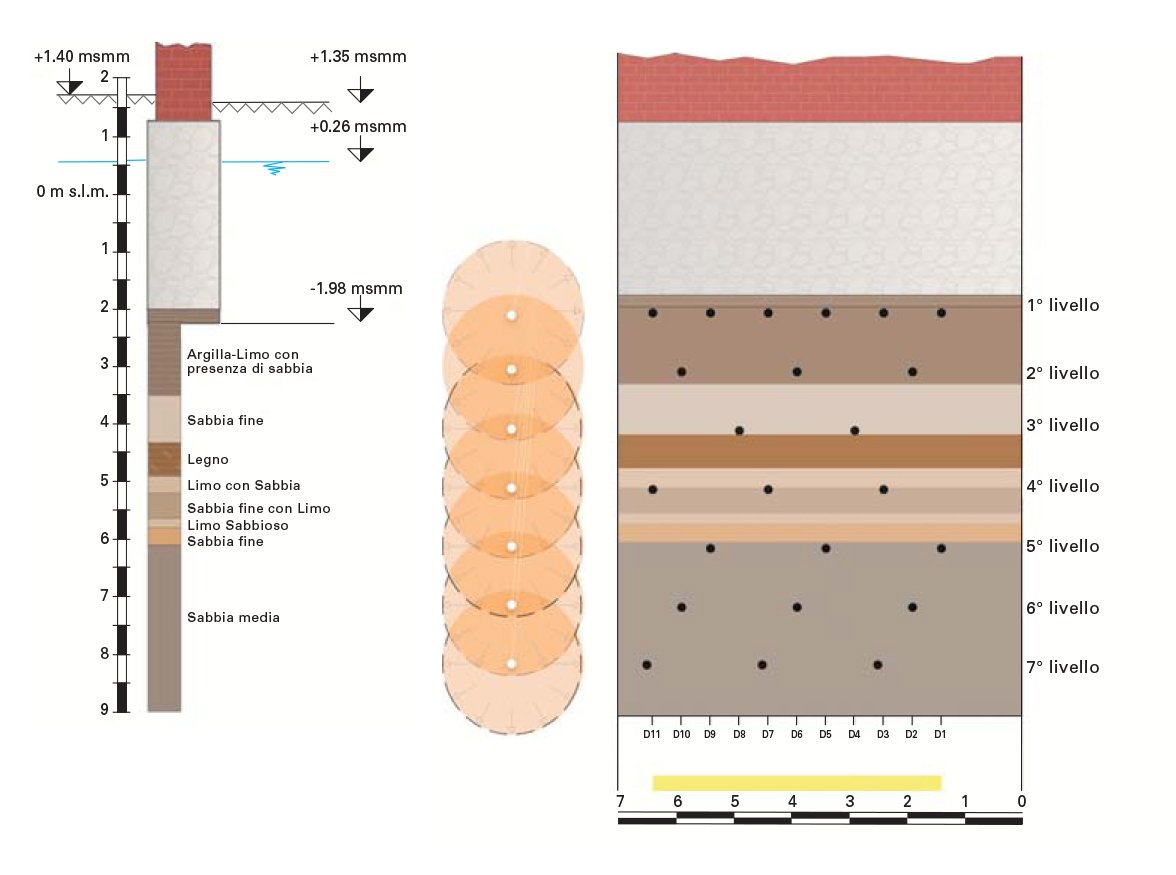
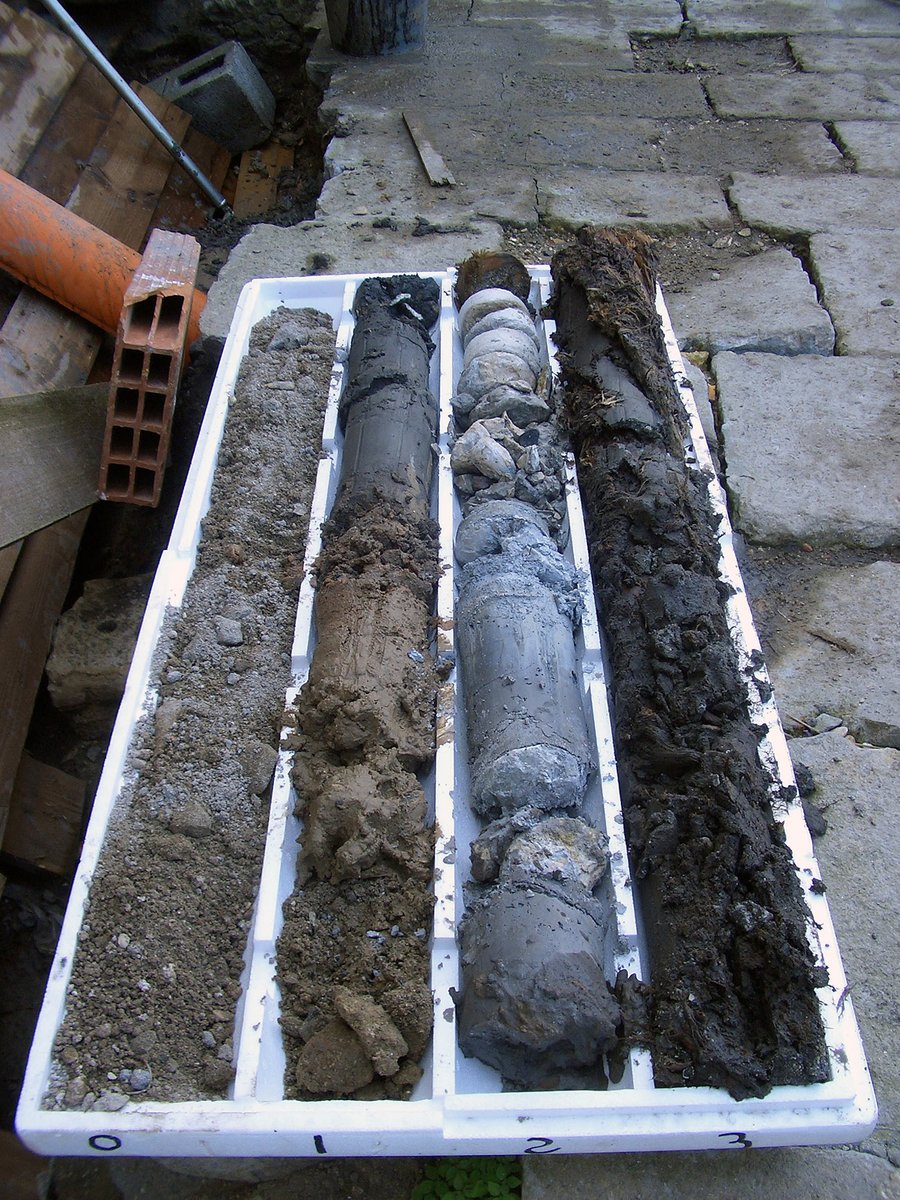
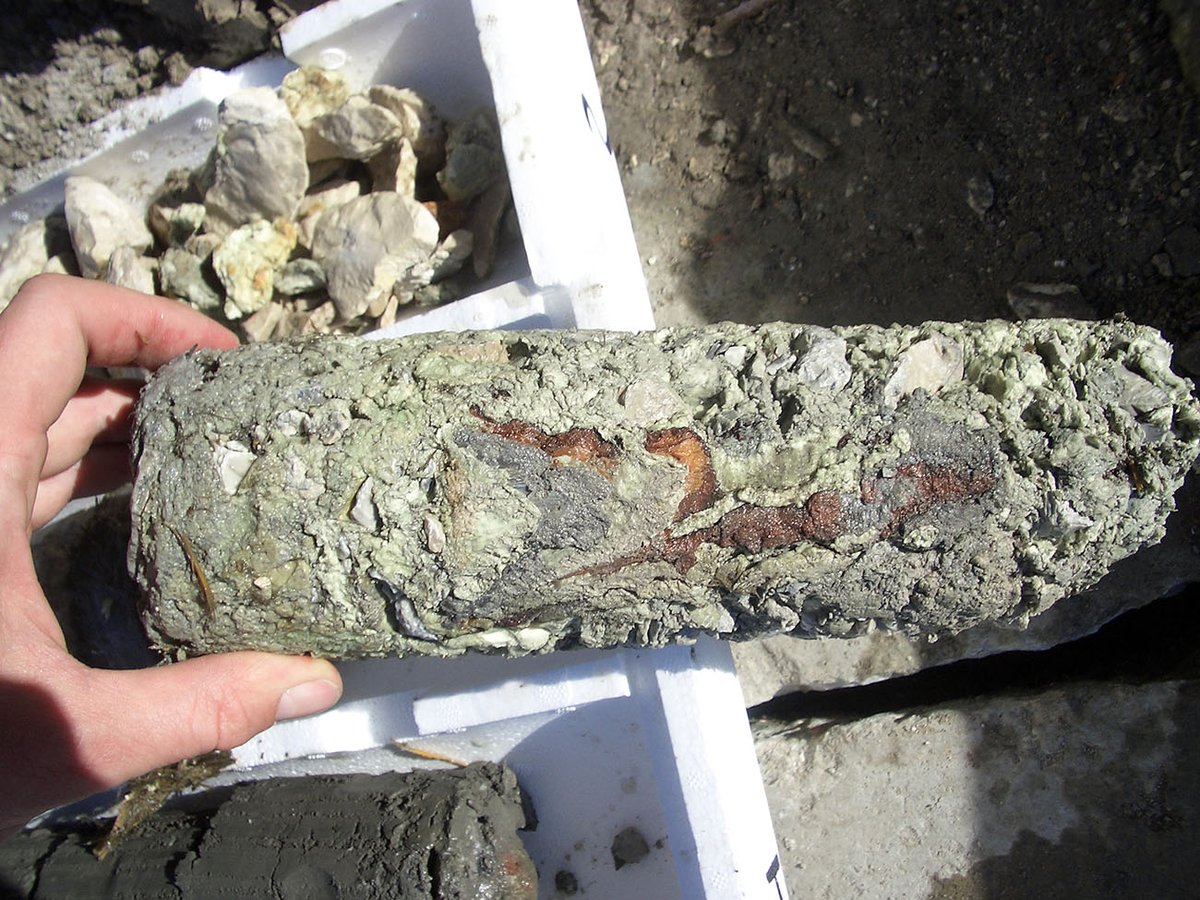
We inspected the foundations using core samples and exploratory wells that revealed great non-uniformity: brick and stone masonry resting directly on the ground, embedded wooden piles, and a portion of the base of a pre-existing tower. We made geognostic investigations (including SPT, CPTu, and laboratory tests) to define the stratigraphy from the quay surface down to 30 m. Before the intervention, we made a series of levelling measurements on the sides of the building facing the canals, which often showed a sudden increase in subsidence between two subsequent readings. The levelling along both sides of the central corridor on the first floor of the building between March and May 2004 showed that the central part of the building had not subsided during the period considered.
The intervention
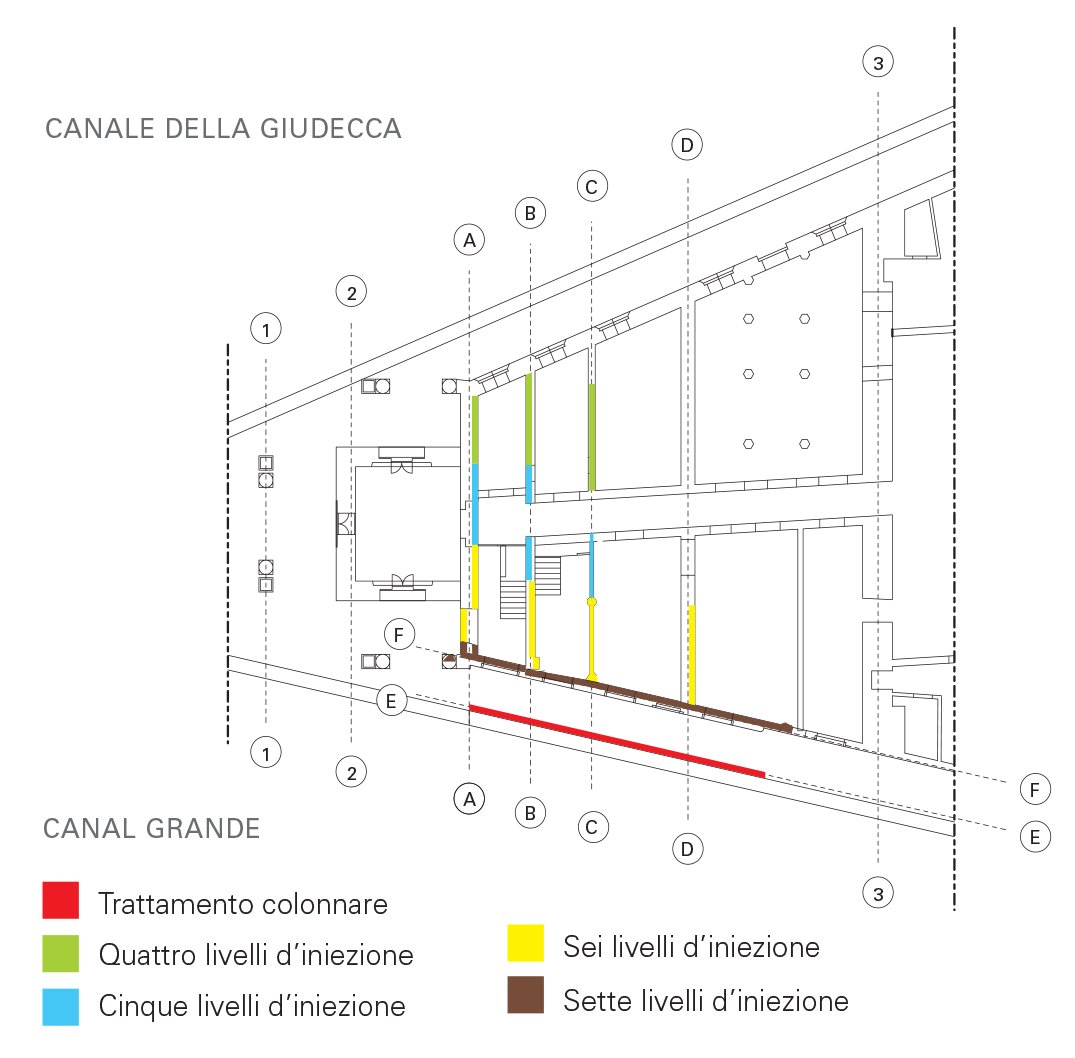
A grid of injections was prepared, distributed over a number of levels ranging from 4 to 7, with inter-hole spacing of about 50 cm. We also made a column-type treatment in which the injection tube was extracted from the hole at a controlled speed as the resin was dispensed. This type of injection involved a strip of land to the rear of the bank wall in the range from -8.50 m to -3.00 m above sea level by means of injection columns with 50 cm spacing.
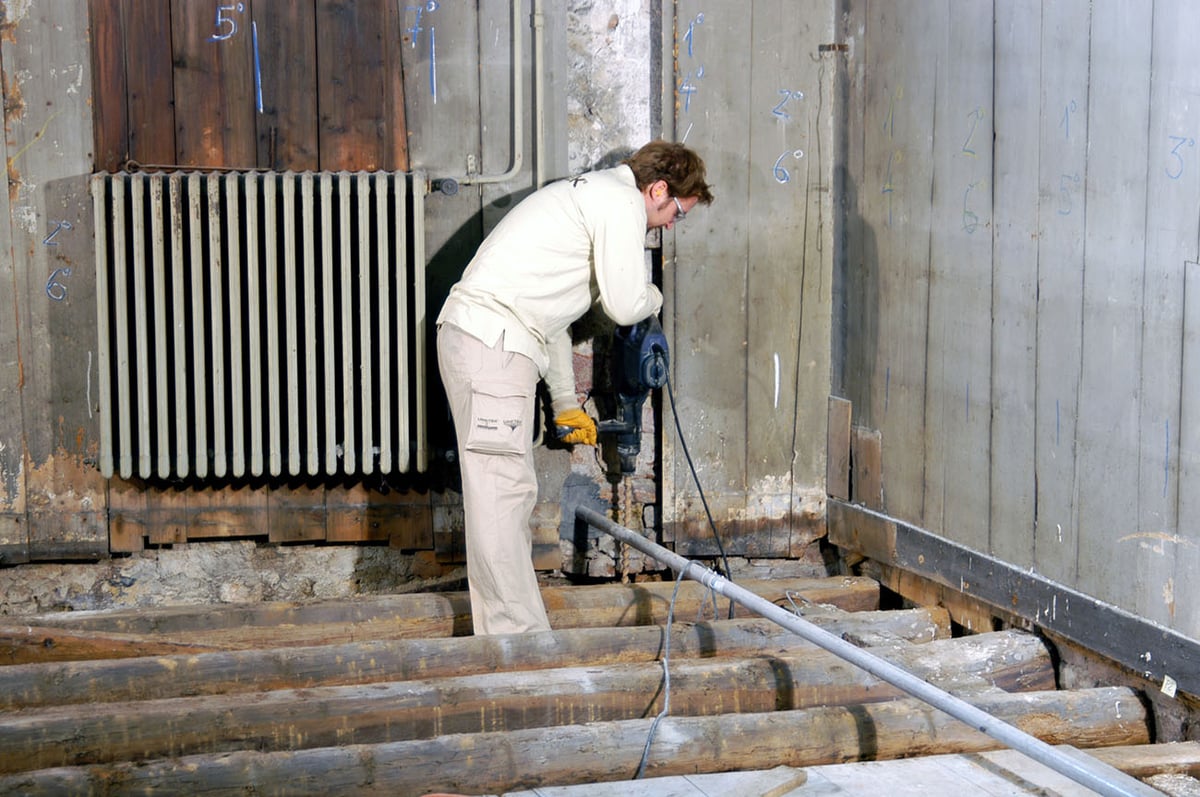






- laser monitoring of the building during injections;
- precision levelling in the part of the building affected by the intervention for 6 months during and after the treatment;
- dynamic penetration tests (DPM 30) before, during, and after the intervention;
- continuous coring and laboratory testing.